Reading notes: Improving Adversarial Robustness (two papers in ICCV 2019)
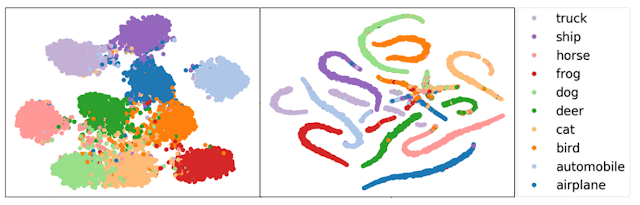
This blog is the reading note for the two papers: "Improving Adversarial Robustness via Guided Complement Entropy" by Hao-Yun Chen, et al., ICCV 2019 and " Adversarial Defense by Restricting the Hidden Space of Deep Neural Networks " by Aamir Mustafa, et al. ICCV 2019. Broadly speaking, these two papers deal with the problem of adversarial attacks on natural images. Specifically, the authors of these two papers both design novel training methods that force the network to learn well-separated feature representations of different classes in some manifolds. This ensures that attackers can no longer fool the network within a restricted perturbation budget. Introduction Deep neural networks are vulnerable to adversarial attacks, which are intentionally crafted to fool them by adding imperceptibly small perturbation to an input image. Several papers have pointed out that the main reason for the existence of such perturbation is the close proximity of different class ...
